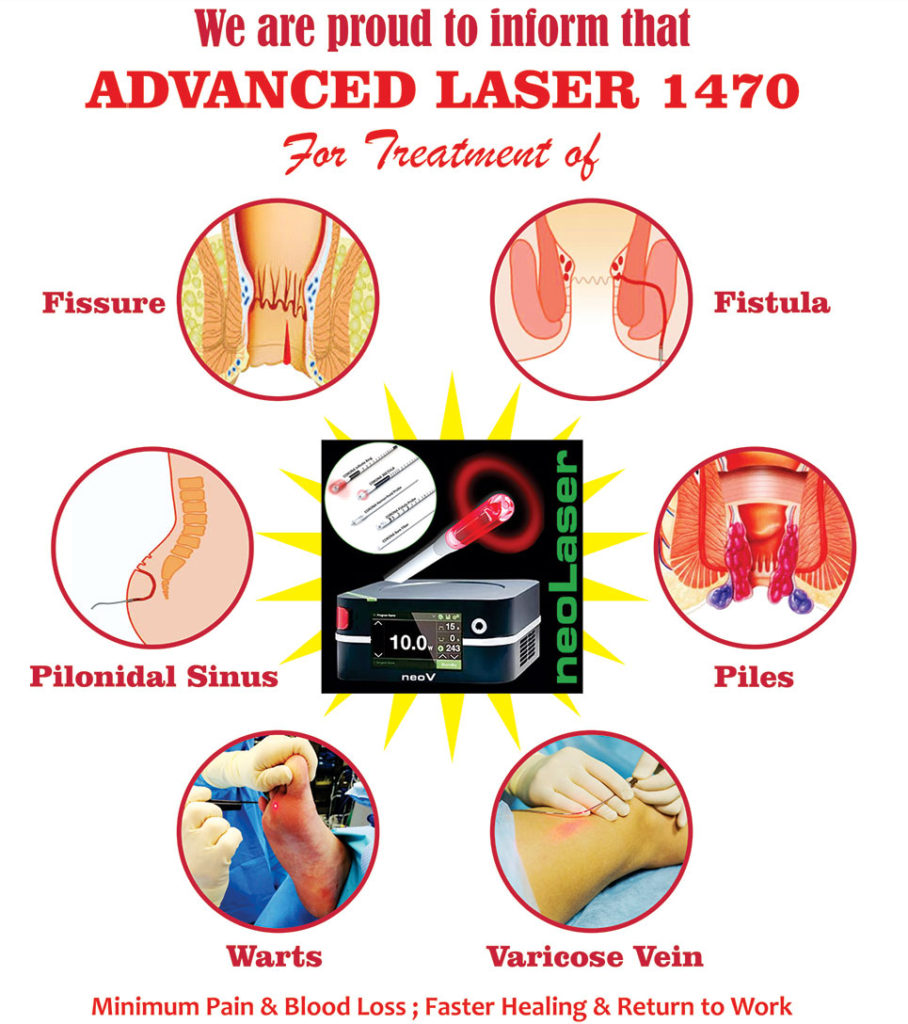
Best Fistula Laser Treatment in Mumbai
Don't wait or self medicate. See a doctor now
What is a fistula?
 The word Fistula means a pipe, tube. Fistula defined as an abnormal passage between interior of the anal canal [or rectum] and the outer skin surface around the anus; A fistula, therefore, consists of –
The word Fistula means a pipe, tube. Fistula defined as an abnormal passage between interior of the anal canal [or rectum] and the outer skin surface around the anus; A fistula, therefore, consists of –
- The internal opening which is inside the anus or rectum,
- The external opening which is on the skin surface around the anus,
- A tube-like structure that connects internal and external opening.
What are the types of fistula ?
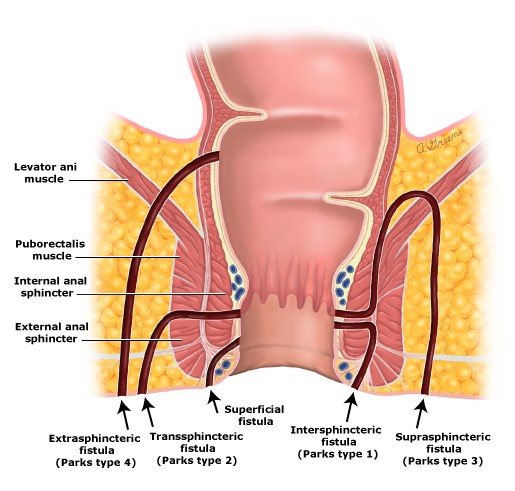
Based on pathogenesis & course of anal fistulae in relation to external sphincter fistulas are classified into the following types
- Intersphincteric
- Transphincteric
- Suprasphincteric
- Extrasphincteric
However for all clinical purposes fistulas are widely divided into:
- Simple fistula
- Complex fistula
Simple Fistula is:
- Low Inter sphincteric (most common)
- Low Transsphincteric
- Single Opening & Tract
- No associated abscess & other specific pathology. (TB, Crohn’s)
- No connection to adjacent structures such as the urinary bladder, etc.
- Non-recurrent
Complex Fistula is:
- High Trans sphincteric (more external sphincter muscle crossed)
- Extra sphincteric
- Supra levator type
- Multiple openings
- Curved or horseshoe shaped tracts
- Associated abscess
- Connection to adjacent structures
- Recurrent Anal Fistula
- Crohn’s Disease, TB, AIDS
- Anteriorly located fistula in females
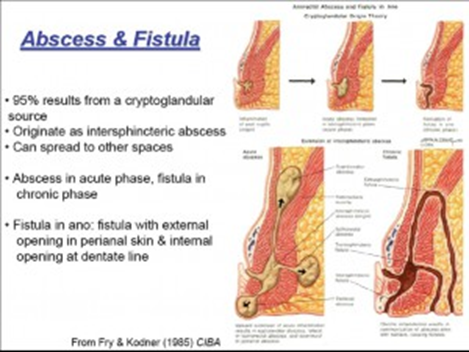
What is Anorectal Abscess and Fistula in ano?
What is an anorectal abscess?
Collection of pus in the potential spaces around the ano-rectum is called an anorectal abscess.
Depending upon the space of collection it is classified into –
- Perianal 60%
- Ischiorectal 30%
- Intersphincteric 5 %
- Supralevator 5%
An abscess & fistula are two phases of the same disease.
Acute is an abscess and when the abscess burst out it forms a chronic discharging fistula.
Infection of the skin around the perineum can also cause an abscess in that area, however, that abscess will not lead to fistula formation. It is said that around 50% to 60 % of the perianal abscess will only develop into a fistula.
What causes abscess & fistula?
The most common cause is an infection of the anal gland (cryptoglandular infection)
The other causes could be:
- Trauma
- Tuberculosis
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn’s disease
- Malignancy
- Lymphogranulomavenereum
- Hydradenitissuppurativa
- Infection of an anal fissure.
- Sexually transmitted infections.
- Diverticulitis
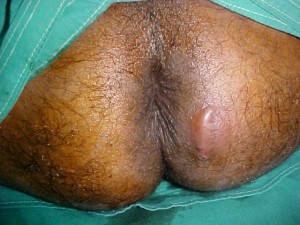 What are the symptoms of an abscess?
What are the symptoms of an abscess?
- Ano-rectal pain
- Swelling and fluctuance
- Drainage of pus and blood
- Fever
- Irritation of skin
- Itching
What is the treatment for anorectal abscess?
- Surgical drainage of the pus is the mainstay of such abscess and should be undertaken earlier than later
- Delay may cause the spread of the infection and its associated consequences
- Appropriate anti-biotics and other supporting treatment are administered at the same time
- 50% of these abscesses later forms a fistula and will require definitive fistula treatment subsequently. The patient should always be informed of this possibility during abscess surgery
- If an experienced surgeon is able to identify the internal opening and is confident of dealing with such fistulous abscess in the same sitting then it can be undertaken to treat the fistula in the same sitting
How to diagnose abscess /fistula in ano?
The most important is a clinical examination by a doctor who would examine and determine the disease present.
Apart from routine blood investigations for an abscess, the specific investigation for fistula includes
- MRI
- Endoanal Ultrasound
- CT scan
- Colonoscopy / Sigmoidoscopy
All these investigations, however, should only be undertaken only after the prescription by a qualified doctor mainly a surgeon dealing with these problems.
What are the symptoms of fistula?
- Presence of a small boil in the perianal area
- Discharge of pus/blood on and off through the boil
- Pain, Itching,
- Bloody Diarrhea / abdominal pain/weight loss may be associated with fistula of specific disease such as TB, Crohn’s etc.
What is the treatment for fistula in ano?
Surgery is the mainstay for complete eradication of fistula in ano.
The primary objective of surgery is to eradicate the infected anal gland and the associated tract/tracts. This has to be achieved while simultaneously preserving anal sphincter muscles which the tract is crossing or else it will lead to incontinence.
Depending upon the type of fistula tract various procedures can be done to achieve the objective:
Simple fistula –
fistulotomy (opening the fistula tract) has been so far described as the gold standard surgery because it has got a very high cure rate and very minimal complications.
Fistulectomy (removal of entire tract) also has a good cure rate however the operating time and healing time are slightly more as also the incidence of minor incontinences as compared to fistulotomy.
Other new sphincter sparing procedures as described below with complex fistula do not have such high cure rate as compared to fistulotomy.
Complex fistula –
The specific cause of fistula such as TB, Crohn’s, etc. needs to be dealt with along with surgery if required.
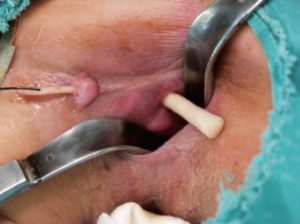
For cryptoglandular fistula the procedures available includes –
- Fistulotomy with primary sphincter repair
- Fistulectomy with primary sphincter repair
The addition of primary sphincter repair to the earlier procedure has shown to improve the results of surgery to as high as 95% with minimal incontinence rates. The healing time is also significantly lessened as compared to the former options. This requires experienced colour [this surgery is undertaken routinely at our centre in view of its high cure rate for complex fistula] - Seton technique (Latin—seta—a bristle) – insertion of thread across the sphincters. This procedure though has got a good cure rate, is plagued by the fact that it causes a lot of pain, discomfort and incontinence. Ayurvedic threads called Ksarshutra are being used by Ayurvedic doctors.
- Mucosal flap procedure
There are other new sphincter sparing procedures such as - GLUE
- Anal Fistula PLUG
- LIFT / BIOLIFT
- VAAFT (endoscopic)
- CELL THERAPY
- Fixicision
- FiLac (LASER)
 Most of these procedures mentioned above do not or minimally damage the sphincter but have a cure rate of around 40 to 70% depending upon the procedures. Some of these procedures like Plug, VAAFT, Cell Therapy, LASER are very costly too thereby limiting their use.
Most of these procedures mentioned above do not or minimally damage the sphincter but have a cure rate of around 40 to 70% depending upon the procedures. Some of these procedures like Plug, VAAFT, Cell Therapy, LASER are very costly too thereby limiting their use.
The choice of the procedure for a particular type of fistula is always decided by the surgeon depending upon the complexity of the disease and his personal training and experience in dealing with the same.
Complications of fi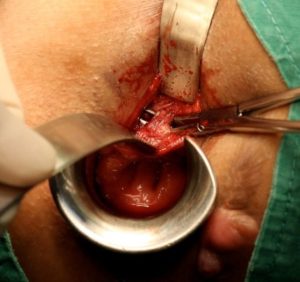 stula
stula
- Recurrence of disease – this is very common in fistula cases and must be understood by the patient before undergoing the same. For simple fistula, the recurrence rate is around 5% if fistulotomy or fistulectomy is done. However, with complex fistula the recurrence rate is almost up to 30 % of cases depending upon the procedure adopted. The least recurrent cases are found with primary sphincter repair surgery.
- Incontinence – that is the loss of control of the passage of stools. The degree varies from minor incontinences which could be just urgency for passing stools and inability to control gases and at times liquid stool especially in diarrhoea to major incontinence such as complete inability to control even solid stools. The sphincter sparing procedure described above causes the least incontinence whereas the others have a varying degree of minor to major incontinences rates.
- The other complication includes bleeding, urinary retention, constipation, delayed healing of the wounds
What will be the duration of hospital stay?
Depending upon the fistula tract and procedure done hospital stay may vary from 1 day to 3 days depending upon the type of fistula and the procedure undertaken along with the general condition of the patient.
Anaesthesia used –
Depending upon the surgeon and the anaesthetist choice, some form of regional anaesthesia like spinal, saddle are used. Some use general anaesthesia. Few opt for local anaesthesia with sedation.
How to take care of the post-operative wound?
The dressing will be done daily by the doctor for some days after the operation and later patient or relative will be educated to do the dressing at home and will be asked to visit the doctor after 2 days or once in a week to assess the wound if any changes are required or not. The patient will be advised daily sitz bath at least 3 times a day. The dressing needs to be done after passage of every stool so that no faecal contamination remains.
Re-joining the Work:
The amount of time you will be off work after surgery depends on both your surgery and your job. This should have been discussed with your doctor before surgery. Most patients are however able to join within a week time to 10 days. The others who can work from home as early as their discharge
Now you have Laser Surgery option too. Please see below image to view the details.